Multithreading in java
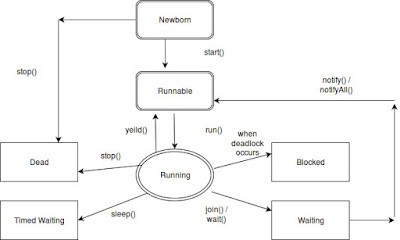
When more than one task is executing concurrently within a single program is called multithreading in Java . Thread in Java is controlled by java.lang.Thread class. Each program can be divided into number of small process . Each small process is called a single thread . Thread is a lightweight process. Thread can be created using this two way .
Example using Runnable interface :
Example using Thread interface :
Find us :
Facebook : @apnaandroid
Google+ : Apna Java
Youtube : Android & Java Tutorial
- implementing Runnable interface
- extending Thread class
- Threads are independent
- Each task of a program can be executed and shared separated memory area.
- It's a lightweight process .
- Communication coast is low between the Threads .
 |
Example using Runnable interface :
public class HelloRunnable implements Runnable {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello from a runnable thread!");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
(new Thread(new HelloRunnable())).start();
}
}
Example using Thread interface :
public class HelloThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello from a thread!");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
(new HelloThread()).start();
}
}
Find us :
Facebook : @apnaandroid
Google+ : Apna Java
Youtube : Android & Java Tutorial


Comments
Post a Comment